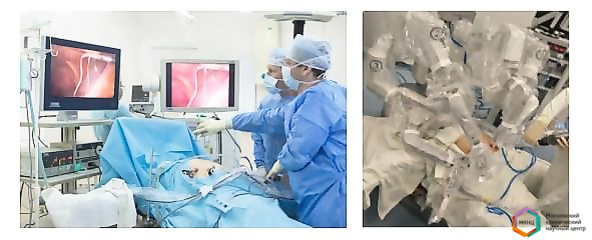
Грыжа пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы
Грыжа пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы (ГПОД) – смещение брюшной части пищевода и желудка в грудную полость через пищеводное отверстие диафрагмы.
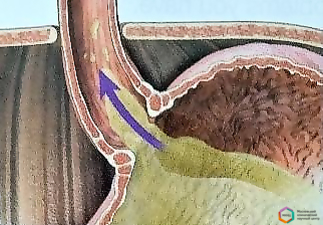
Осложнения ГЭРБ:
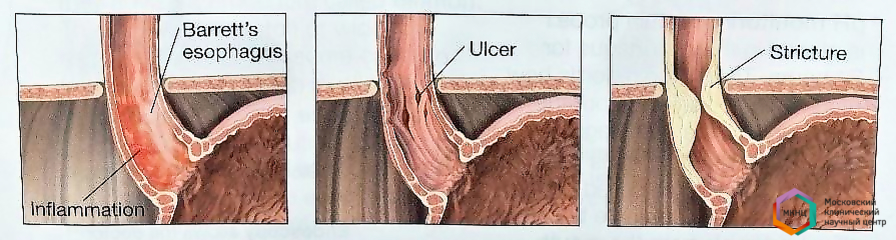
- Эрозии и язва пищевода.
- Стриктура пищевода.
- Пищевод Барета (предраковое состояние).
- Ущемление органов брюшной полости (при параэзофагеальных грыжах).
Распространение ГЭРБ во всем мире от 8-27,8 % на 100 тыс. населения.
В России составляет 23.7 % на 100 тыс. населения.
А) Скользящие - часть пищевода и желудка в вертикальной положении возвращаются в брюшную полость.
Б) Фиксированные - часть пищевода и желудок остаются в грудной полости (фиксированы спайками).
А) Кардиальные – смещается только кардиальный отдел желудка.
Б) Кардифундальные – смещается кардиальный отдел и дно желудка.
В) Субтотальные – 2/3 желудка расположены выше диафрагмы.
Г) Тотальные – весь желудок расположен выше диафрагмы.
Д) Параэзофагеальные – кардиальная часть желудка остается в брюшной полости, а органы брюшной полости (желудок, толстая кишка, большой сальник) смещаются выше диафрагмы.
Факторы риска.
- Повышенная масса тела.
- Прием жирной пищи, кофе и газированных напитков.
- Употребление алкогольных напитков.
- Курение.
Симптомы.
1. Пищеводные симптомы.
- Изжога.
- Отрыжка, регургитация (заброс ранее съеденной пищи).
- Дисфагия.
2. Внепищеводные симптомы.
- Кашель и хрипы.
- Охриплость, боль в горле.
- Отиты.
- Некардиальная загрудинная боль.
- Эрозии зубной эмали и другие проявления со стороны зубов.
- Анемия.
Диагностика.
- Рентгенологическое исследование с контрастным веществом (полипозиционное).
- ЭГДС (при необходимости взятие биопсии).
- Манометрия пищевода (исследование моторики пищевода).
- Суточная рН-метрия.
Лечение.
Основным методом лечения является комплексное лекарственная терапия.
При неэффективности курса терапии и наличие осложнений – показано хирургическое лечение.
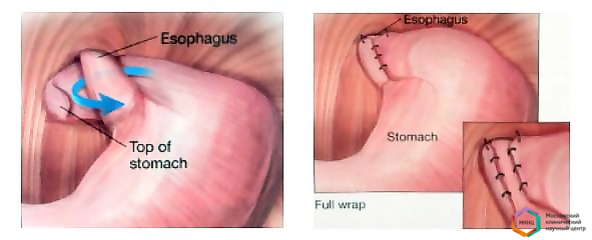
Операция направленная на устранение рефлюкса называется фундопликация.
Основные виды фундопликаций:
1. Фундопликация по Nissen, по А.Ф. Черноусову (фундопликации 360* циркулярные).
2. Фундопликации по Toupet ( фундопликации 270* парциальные).
Выбор вида фундопликации проводится только после комплексного диагностического обследования.
Сотрудники отделения высокотехнологичной хирургии МКНЦ им. А.С. Логинова данные операции выполняют из малотравматичных доступов (лапароскопические операции, роботические операции).
Послеоперационный период составляет 1-2 дня.
Период реабилитации 1-1,5 нед.