Carotid artery atherosclerosis
What is carotid artery atherosclerosis?
One of the most common causes of arterial damage is atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease that results in abnormal deposition of cholesterol and fat on the inner wall of the artery, which leads to the formation of plaques. Over time, the plaque grows, blocks the internal lumen of the artery, and obstructs blood flow as a result. Atherosclerosis affects all the arteries that supply blood to the brain - the vertebral and carotid; the aorta and the arteries of the lower extremities, as well as the arteries that supply the internal organs - the visceral and renal arteries.
What is the danger of atherosclerosis?
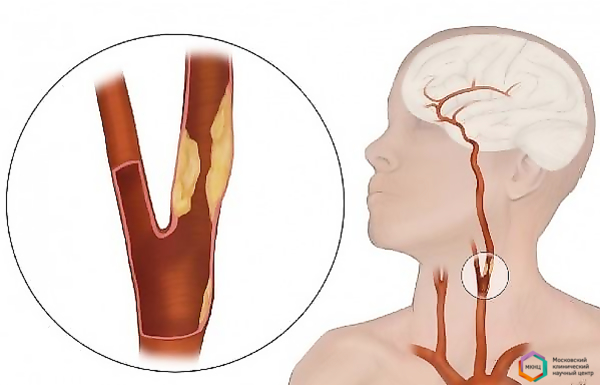 Due to the narrowing of the carotid arteries, the blood supply to the brain is sharply reduced and a stroke(acute violation of cerebral circulation or violation of cerebral circulation) can occur with a variety of motor and sensory disorders, up to paralysis, speech disorders. Sometimes a fragment or blood clot breaks off from the surface of the atherosclerotic plaque of the carotid artery, leading to the same consequences. In 70% of cases, a brain stroke develops without any harbingers, and in 40% of cases, a stroke leads to the death of a person. It is believed that after narrowing the lumen of the artery by more than 60%, the probability of developing a stroke increases dramatically.
Due to the narrowing of the carotid arteries, the blood supply to the brain is sharply reduced and a stroke(acute violation of cerebral circulation or violation of cerebral circulation) can occur with a variety of motor and sensory disorders, up to paralysis, speech disorders. Sometimes a fragment or blood clot breaks off from the surface of the atherosclerotic plaque of the carotid artery, leading to the same consequences. In 70% of cases, a brain stroke develops without any harbingers, and in 40% of cases, a stroke leads to the death of a person. It is believed that after narrowing the lumen of the artery by more than 60%, the probability of developing a stroke increases dramatically.
Who may be at risk.
The following groups of patients are at greater risk of carotid artery atherosclerosis:
-
with high blood pressure
-
with high cholesterol in the blood
-
with diabetes mellitus
-
with obesity
-
smokers, etc.
Symptoms of arterial damage.
Important to know! Carotid artery disease often occurs without any complaints or symptoms!
Who should see a doctor and what examinations should I undergo?
If there are predisposing factors in your life:
-
age over 55,
-
smoking,
-
hypercholesterolemia (abnormal increase in the level of cholesterol in the blood),
-
hereditary predisposition (stroke or heart attack in relatives),
you need to undergo a special study-a duplex scan of the carotid arteries (brachiocephalic) and seek the advice of a vascular surgeon.
Indications for surgical treatment.
Large-hemodynamically significant, i.e. disrupting the flow of blood through the carotid artery - atherosclerotic plaques are an indication for surgical treatment to prevent the development of stroke.
Possibilities of surgical treatment.
There are several types of surgical treatment:
-
open surgical removal of plaque from the lumen of the artery (carotid endarterectomy)
-
endovascular treatment - placing a stent in the lumen of the vessel.
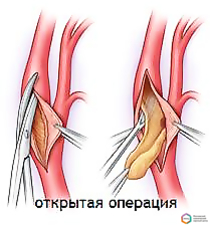
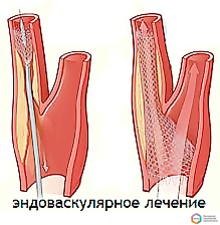
The surgeon decides on the scope and type of surgical treatment based on the results of the examination.
Possible consequences of the operation.
These operations are usually safe. The probability of developing complications is estimated as 1-2%. The most important thing is that in the future, repeated narrowing usually does not occur and strokes do not develop.
The history of the MCSC patient.
A 70-year-old man turned to the MCSC. He had previously suffered a stroke due to blocked blood flow through the right internal carotid artery. As a result, the right arm and leg began to work poorly. With a diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, he was admitted to the Department of Vascular Surgery of the MCSC.
Specialists of the MCSC diagnosed atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries:atherosclerotic stenosis (narrowing to a minimum) of the left internal carotid artery by 90%, - and performed a kkb carotid endarterectomy (direct removal of atherosclerotic plaque from the affected artery) to prevent a left stroke. The patient was successfully operated on in our Center.

The rehabilitation was easy. On the fifth day, the patient was discharged and returned home without assistance.
The doctors of the Department of vascular surgery managed to improve the quality of life of the patient and prevent a second stroke.





